In the application field of falling film evaporators, film distribution uniformity and heat transfer efficiency have always been core bottlenecks restricting equipment performance. Due to design limitations, traditional old-style film distributors generally suffer from problems such as insufficient film distribution, uneven distribution, and easy blockage, resulting in low heat transfer coefficients and directly affecting evaporation efficiency and energy consumption levels. These have become long-standing technical pain points difficult to overcome in the industry.
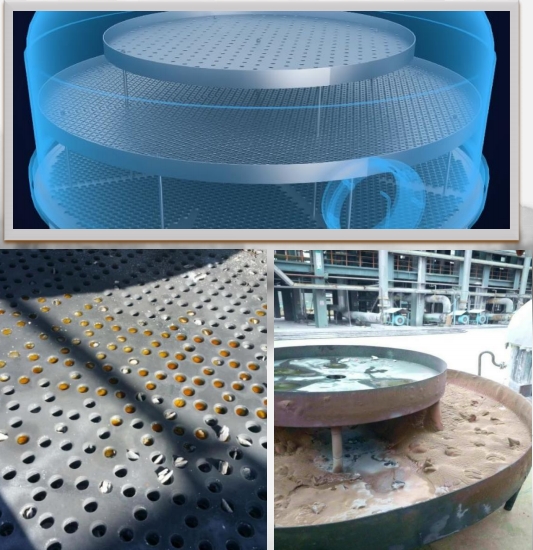
As an innovation leader in the chemical equipment field, relying on deep insights into industry needs and technical accumulation, Jiuye Chemical has successfully developed a new type of film distributor. Through disruptive design, it reconstructs the film distribution logic, breaks through traditional technical barriers at one stroke, and brings a revolutionary solution to the performance upgrade of falling film evaporators!
Ⅰ. Analysis of the Three Pain Points of Traditional Film Distributors
1. Insufficient Film Distribution
The old-style film distributors have irrational aperture layouts and single liquid distribution paths, making them prone to forming local liquid accumulation or blank areas. This results in the surface of the evaporation tube not being fully covered by the liquid film, leading to insufficient utilization of the heat transfer area.
2. Uneven Film Distribution
The traditional structure makes it difficult to precisely control the liquid flow rate and velocity, resulting in uneven circumferential distribution of the liquid film thickness on the evaporation tube and even the occurrence of "dry wall" phenomenon, which significantly reduces the heat transfer coefficient (according to measurements, the heat transfer coefficient of traditional film distributors can fluctuate by 20%-30%).
3. Prone to Blockage and Scaling
The fixed aperture design has poor adaptability to high-concentration materials containing particles, as impurities or crystallites in the liquid are prone to (stagnation and blockage). This not only affects the stability of film distribution but also requires frequent shutdowns for cleaning, increasing operational and maintenance costs.
Ⅱ. Jiuye's New Film Distributor: Three Innovations Reconstructing Technical Logic
1. Optimized Aperture Matrix Design
- Asymmetric aperture arrangement: A radial aperture matrix of "sparse center - dense edge" is adopted. According to the results of fluid mechanics simulation, the flow is accurately allocated to ensure that the liquid evenly covers the entire surface of the evaporation tube from the outlet of the film distributor, eliminating circumferential film distribution deviation.
- Variable-diameter channel structure: The inlet end adopts a converging channel design, which enhances the turbulence intensity of the liquid through flow velocity gradient regulation, reduces the risk of impurity retention, and adapts to working conditions with high-viscosity and solid-content materials.
2. Film Distribution Stratified Diversion Technology
- Multi-level diversion channels: The innovative "main film distribution layer + auxiliary diversion layer" dual-structure design is introduced. The main layer achieves basic liquid film distribution, while the auxiliary layer uses inclined diversion grooves to secondary-homogenize the liquid flow, forming a uniform-thickness (deviation ≤5%), continuous and stable liquid film.
- Dynamic adaptive adjustment: The angle and spacing of the diversion grooves can be flexibly adjusted according to material characteristics (such as viscosity and concentration). Through modular design, the film distribution effect under different working conditions is optimized, breaking through the limitation of the traditional film distributor's "one device for one use".
3. Anti-blocking Self-cleaning Mechanism
- Curved anti-scaling inner wall: The interior of the film distributor adopts a streamlined curved surface structure to reduce dead corners of liquid retention. Combined with the pulsed backflushing design at the end of the aperture, it can automatically remove attached crystallites or impurity particles.
- Online monitoring and intelligent control: Integrated with pressure sensors and flow monitoring modules to provide real-time feedback on the film distribution status. When a blockage risk is detected, the automatic backflushing program is activated, completing cleaning without shutdown and enhancing the continuous operation capability of the equipment.
Ⅲ. Application Scenarios and Customer Value
- High-concentration material evaporation: Suitable for processing high-salt and high-viscosity materials in industries such as alumina, chemical engineering, and pharmaceuticals, including sodium aluminate solution, waste acid liquid, traditional Chinese medicine concentrated solution, etc. It solves the problem of film distribution failure of traditional equipment under high-concentration working conditions.
- Energy-saving and efficiency-boosting upgrade: Application cases of an alumina enterprise show that after replacing with Jiuye's new film distributor, a single evaporator can save over 2 million yuan in steam costs annually, with a production capacity increase of 18% and an overall equipment efficiency (OEE) improvement of 25%.
- Long-period stable operation**: The anti-blocking design extends the continuous operation cycle of the equipment from the traditional 1-2 months to 6-12 months, significantly reducing shutdown maintenance costs. It is particularly suitable for highly automated continuous production scenarios.
Ⅳ. Leading Technology, Redefining Film Distribution Standards
The successful development of Jiuye's new film distributor is not only an innovation in the core components of falling film evaporators but also marks China's independent breakthrough in key technologies of high-end chemical equipment. At present, this technology has obtained multiple national invention patents, passed pilot and industrial verification, and is being rapidly promoted in industries such as alumina and new energy materials.